코딩로그
10. Neural Network 2: ReLU and 초기값 정하기 본문
-
계층을 늘려 XOR문제를 풀었던 것처럼 신경망이 깊어져야 복잡한 문제를 풀 수 있다.
-
기존의 방법으로 신경망의 깊이만 깊게하자 문제를 제대로 풀기가 어려웠다.
-
신경망의 계층을 늘리기가 어려워지자 인공지능의 2차 겨울이 찾아왔다.
-
오늘은 이를 극복한 방법에 대해 이야기해보겠다.
1. rulu fuction
-
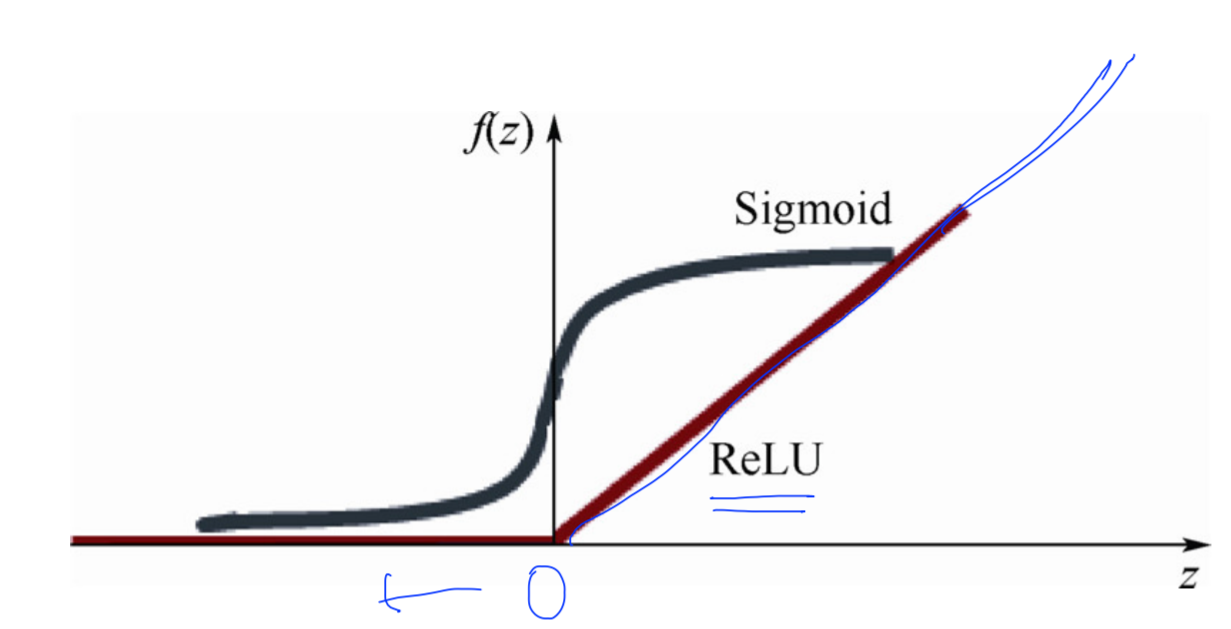
sigmoid함수 ->0~1사이 값이다.
-
따라서 층이 깊어질수록 값이 점점 작아진다.
-
relu라는 activation function을 만들었다.
-
0보다 작으면 0이고 그 이상이면 값을 그대로 반환한다.
-
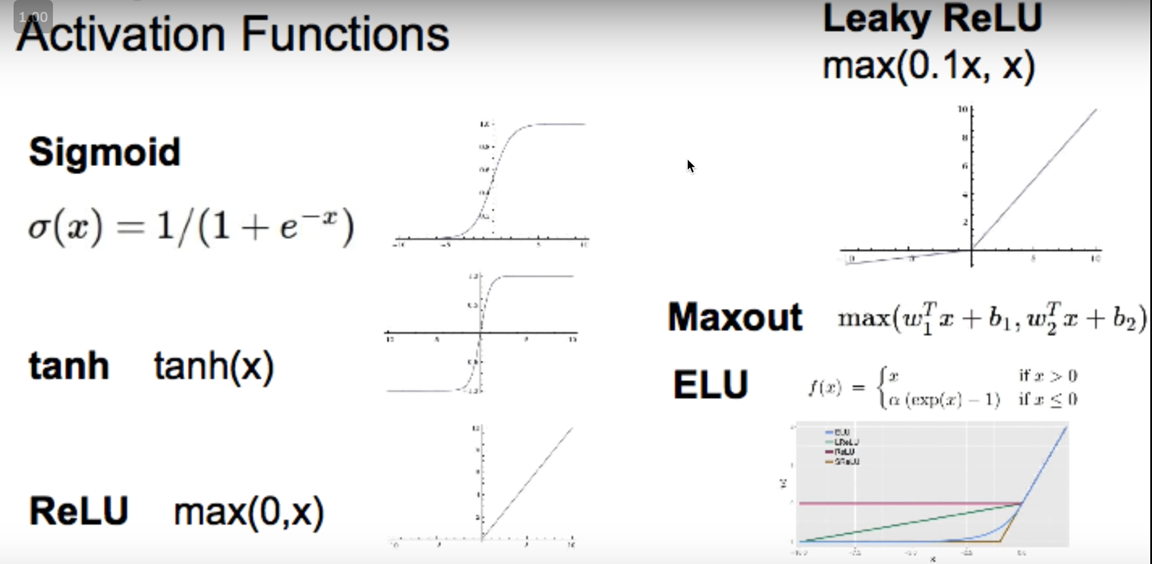
이외에도 relu함수를 변형한 다양한 함수가 있다.
-
leaky relu함수 : 0이하의 값도 어느정도 value를 갖도록 함.
-
ELU : leaky relu의 경우 최솟값이 0.1x로 정해져 있음. 이걸 수정해서 사용할 수 있도록 함.
-
Maxout : 이것 또한 최솟값과 최댓값을 수정할 수 있도록 하는 activation function
-
tanh : -1에서 1사이의 값이 나올 수 있도록 하는 sigmoid와 비슷하게 생긴 activation function
2. weight 값을 잘 주기
- 또한 weight을 잘못 주었기 때문에 잘 작동하지 않았다는 것을 알게 되었다. 그렇다면 weight을 어떻게 주어야 할까?
- 만약 0으로 준다면 ? -> 이어진 신경망의 값도 모두 0이되는 문제 발생 (신호가 없어짐)
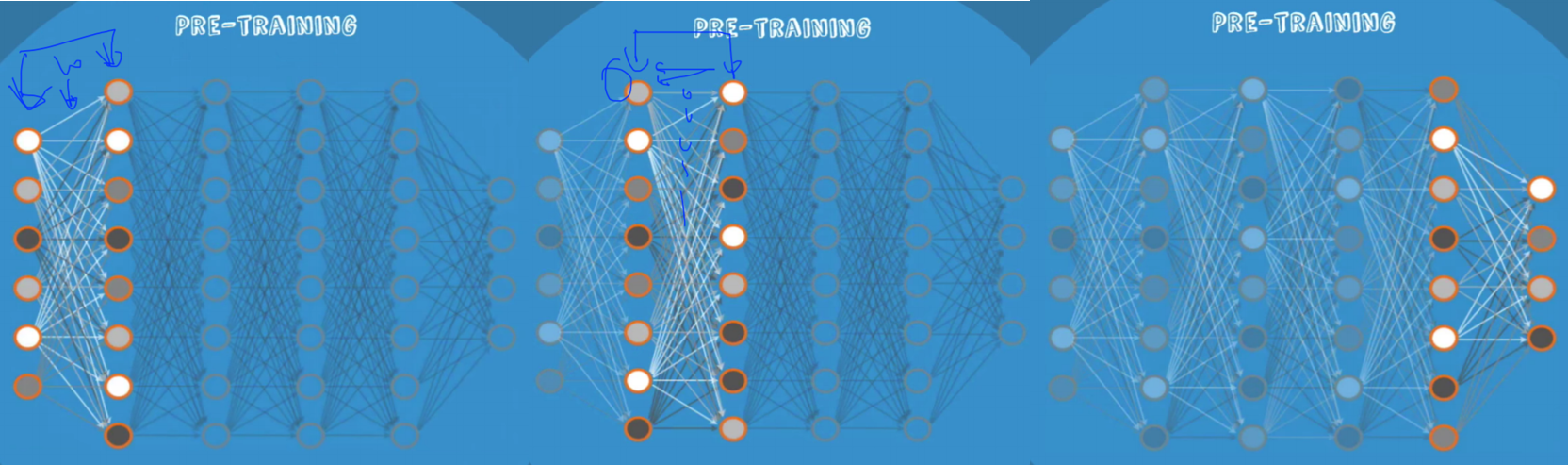
- weight을 잘 주는 방법 : RBM, RBM을 통해 만들어진 neural net-> deep belief net
- RBM 작동 원리
- pre-training : 딱 두 개의 층에서만 forward 와 backpropagation을 반복해 w와 b의 초깃값을 설정한다.
- fine tunning : 초깃값이 잘 설정되어 있기 때문에 나중의 학습 과정을 training이 아닌 fine tunning이라고 부를 정도임.
- 쓰지 않아도 된다 ? : 노드의 입력값과 출력값을 생각해서 초깃값을 간단하게 주기만 해도 된다.
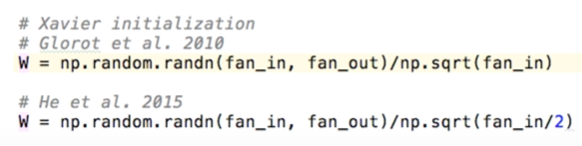
- 밑과 같은 초깃값을 주면 된다. (하단처럼 /2를 해주면 더욱 잘 작동한다.)
- fan_in은 노드에 들어오는 입력값의 갯수, fan_out은 노드에서 나오는 출력값의 갯수이다.
- 여러 가지를 시도해보고 자신에게 맞는 방법을 찾아가자 !
2. dropout모델과 앙상블
-
training set에 대해서는 높은 정확도를 보이나 test set에 대해서는 낮은 정확도를 보이는 경우가 있다.
-
많은 training을 거칠수록 오히려 test set에서는 더 오차율이 높아지는 것 : overfitting이다.
-
따라서 이전에 배웠던 regularization을 해야한다 ! 지난 시간에 배웠으므로 생략하겠다.
-
기억이 잘 나지 않는다면 본 링크를 통해 복습을 하자 !
https://jumpjump3030.tistory.com/20
7-1. ML의 실용과 몇가지 팁
이번 시간에는 효율적인 ML을 위한 몇가지 팁에 대해 알아보겠다. Learning rate : $W := W-\alpha \frac{\partial }{\partial W}cost(W)$ 에서 알파에 해당하는 값..
jumpjump3030.tistory.com
-
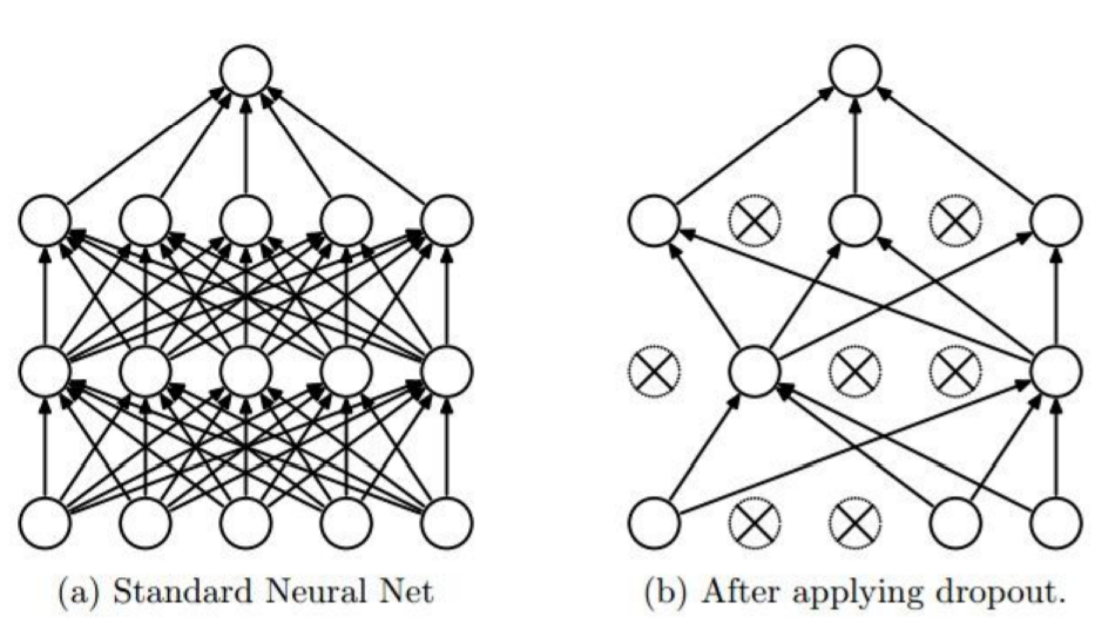
overfitting을 방지할 수 있는 또 다른 방법은 바로 dropout이다.
-
dropout : 몇가지 뉴런을 zero로 처리해버리는, 즉 training에 관여하지 않도록 하는 것. training때마다 랜덤하게 zero로 처리하는 데이터를 정한다.
-
주의할 점 : 평가 or test할 때는 dropout_rate를 1로 반드시 주어야 한다. !
- regularization을 위한 또다른 스킬들이 있다.
- fast forward : 모든 노드를 하나하나 거치지 않고 건너뛰면서 거치는 것이다. 즉, 거리가 먼 노드도 서로 더 큰 영향을 줄 수 있다.
- split&merge : 전파가 나눠서 가다가 다시 만나는 과정을 반복 or 변수마다 신경망을 나누어서 계산하고 나중에 합치는 것이다!
- recurrent network : 앞이 아닌 옆으로도 신경망의 방향을 조정하는 것이다.
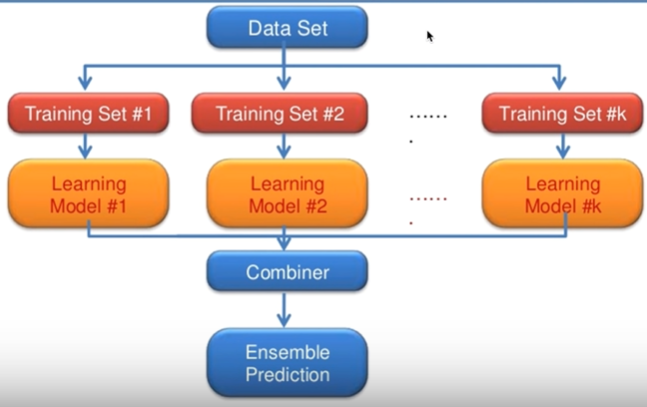
- 앙상블 : 여러 가지 모델을 합쳐서 ensemble prediction을 내보자 !
<실습 - 딥러닝으로 MNIST 98%이상 해보기>
- 지난번 softmax로 분류했던 mnist를 neural net과 여러가지 스킬을 통해 분석해보겠다. 혹시 기억이 잘 나지 않는다면 링크를 참고하자.
https://jumpjump3030.tistory.com/21
7-2. ML의 실용 : mnist data set 실습
내용이 많아 mnist 실습은 따로 올렸습니다. <실습 - mnist data/test set> mnist dataset : 손으로 쓴 숫자를 판별하는 data set 28X28 픽셀로 shape(?,784)의 특성을 갖는다. -> ?는 트레이닝 데이터의 개수이다..
jumpjump3030.tistory.com
1. 신경망을 활용한 mnist 분석
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
|
# Lab 10 MNIST and NN
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import random
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.set_random_seed(777) # reproducibility
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# input place holders
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# weights & bias for nn layers
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 256]))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256]))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 256]))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256]))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2) + b2)
W3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 10]))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
hypothesis = tf.matmul(L2, W3) + b3
# define cost/loss & optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=hypothesis, labels=Y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# initialize
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# train my model
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys}
c, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# Test model and check accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print('Accuracy:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}))
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r + 1], 1)))
print("Prediction: ", sess.run(
tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r + 1]}))
# plt.imshow(mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].
# reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
# plt.show()
'''
Epoch: 0001 cost = 141.207671860
Epoch: 0002 cost = 38.788445864
Epoch: 0003 cost = 23.977515479
Epoch: 0004 cost = 16.315132428
Epoch: 0005 cost = 11.702554882
Epoch: 0006 cost = 8.573139748
Epoch: 0007 cost = 6.370995680
Epoch: 0008 cost = 4.537178684
Epoch: 0009 cost = 3.216900532
Epoch: 0010 cost = 2.329708954
Epoch: 0011 cost = 1.715552875
Epoch: 0012 cost = 1.189857912
Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.820965160
Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.624131458
Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.454633765
Learning Finished!
Accuracy: 0.9455
'''
|
cs |
2. Relu function을 활용한 mnist 분석
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
|
# Lab 10 MNIST and Xavier
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.set_random_seed(777) # reproducibility
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# input place holders
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", shape=[784, 256],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256]))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", shape=[256, 256],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256]))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2) + b2)
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", shape=[256, 10],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
hypothesis = tf.matmul(L2, W3) + b3
# define cost/loss & optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=hypothesis, labels=Y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# initialize
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# train my model
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys}
c, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# Test model and check accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print('Accuracy:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}))
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r + 1], 1)))
print("Prediction: ", sess.run(
tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r + 1]}))
# plt.imshow(mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].
# reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
# plt.show()
'''
Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.301498963
Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.107252513
Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.064888892
Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.044463030
Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.029951642
Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.020663404
Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.015853033
Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.011764387
Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.008598264
Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.007383116
Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.006839140
Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.004672963
Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.003979437
Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.002714260
Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.004707661
Learning Finished!
Accuracy: 0.9783
'''
|
cs |
3. Xavier initialization을 이용한 초깃값 설정
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
|
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import random
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.set_random_seed(777) # reproducibility
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
# input place holders
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", shape=[784, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2) + b2)
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L2, W3) + b3)
W4 = tf.get_variable("W4", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L3, W4) + b4)
W5 = tf.get_variable("W5", shape=[512, 10],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b5 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
hypothesis = tf.matmul(L4, W5) + b5
# define cost/loss & optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=hypothesis, labels=Y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# initialize
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# train my model
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys}
c, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# Test model and check accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print('Accuracy:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}))
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r + 1], 1)))
print("Prediction: ", sess.run(
tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r + 1]}))
# plt.imshow(mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].
# reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
# plt.show()
'''
Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.266061549
Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.080796588
Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.049075800
Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.034772298
Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.024780529
Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.017072763
Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.014031383
Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.013763446
Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.009164047
Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.008291388
Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.007319742
Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.006434021
Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.005684378
Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.004781207
Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.004342310
Learning Finished!
Accuracy: 0.9742
'''
|
cs |
4. dropout을 활용한 mnist 분석
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
# Lab 10 MNIST and Dropout
import tensorflow as tf
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.set_random_seed(777) # reproducibility
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
# input place holders
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# dropout (keep_prob) rate 0.7 on training, but should be 1 for testing
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", shape=[784, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
L1 = tf.nn.dropout(L1, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2) + b2)
L2 = tf.nn.dropout(L2, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L2, W3) + b3)
L3 = tf.nn.dropout(L3, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W4 = tf.get_variable("W4", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L3, W4) + b4)
L4 = tf.nn.dropout(L4, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W5 = tf.get_variable("W5", shape=[512, 10],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b5 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
hypothesis = tf.matmul(L4, W5) + b5
# define cost/loss & optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=hypothesis, labels=Y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# initialize
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# train my model
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 0.7}
c, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
# Test model and check accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print('Accuracy:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1}))
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r + 1], 1)))
print("Prediction: ", sess.run(
tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r + 1], keep_prob: 1}))
# plt.imshow(mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].
# reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
# plt.show()
'''
Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.447322626
Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.157285590
Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.121884535
Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.098128681
Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.082901778
Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.075337573
Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.069752543
Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.060884363
Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.055276413
Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.054631256
Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.049675195
Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.049125314
Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.047231930
Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.041290121
Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.043621063
Learning Finished!
Accuracy: 0.9804
'''
|
cs |
'코딩로그 > 모두를 위한 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 11. Convolutional Neural Networks(실습) (0) | 2020.02.01 |
|---|---|
| 11. Convolutional Neural Networks (0) | 2020.02.01 |
| 9. Neural Network 1: XOR 문제와 학습방법, Backpropagation (0) | 2020.01.27 |
| 8. 딥러닝의 기본 개념과, 문제, 그리고 해결 (0) | 2020.01.11 |
| 7-2. ML의 실용 : mnist data set 실습 (0) | 2020.01.11 |



