코딩로그
7-2. ML의 실용 : mnist data set 실습 본문
- 내용이 많아 mnist 실습은 따로 올렸습니다.
<실습 - mnist data/test set>
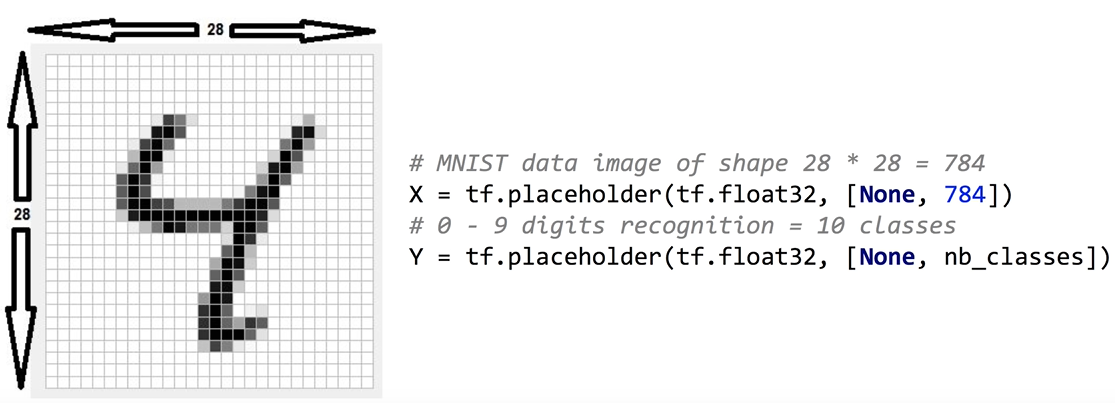
- mnist dataset : 손으로 쓴 숫자를 판별하는 data set
- 28X28 픽셀로 shape(?,784)의 특성을 갖는다. -> ?는 트레이닝 데이터의 개수이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import ssl
ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# mnist data를 읽어옴.
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
nb_classes = 10
# MNIST data image of shape 28 * 28 = 784
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
# 0 - 9 digits recognition = 10 classes
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, nb_classes])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, nb_classes]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([nb_classes]))
# Hypothesis (using softmax)
hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X, W) + b)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(Y * tf.log(hypothesis), axis=1))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(cost)
# Test model
is_correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
# Calculate accuracy
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct, tf.float32))
# parameters
num_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
num_iterations = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initialize TensorFlow variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in range(num_iterations):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, cost_val = sess.run([train, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys})
avg_cost += cost_val / num_iterations
print("Epoch: {:04d}, Cost: {:.9f}".format(epoch + 1, avg_cost))
print("Learning finished")
# Test the model using test sets
print(
"Accuracy: ",
accuracy.eval(
session=sess, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}
),
)
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r : r + 1], 1)))
print(
"Prediction: ",
sess.run(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r : r + 1]}),
)
plt.imshow(
mnist.test.images[r : r + 1].reshape(28, 28),
cmap="Greys",
interpolation="nearest",
)
plt.show()
'''
Epoch: 0001, Cost: 2.826302672
Epoch: 0002, Cost: 1.061668952
Epoch: 0003, Cost: 0.838061315
Epoch: 0004, Cost: 0.733232745
Epoch: 0005, Cost: 0.669279885
Epoch: 0006, Cost: 0.624611836
Epoch: 0007, Cost: 0.591160344
Epoch: 0008, Cost: 0.563868987
Epoch: 0009, Cost: 0.541745171
Epoch: 0010, Cost: 0.522673578
Epoch: 0011, Cost: 0.506782325
Epoch: 0012, Cost: 0.492447643
Epoch: 0013, Cost: 0.479955837
Epoch: 0014, Cost: 0.468893674
Epoch: 0015, Cost: 0.458703488
Learning finished
Accuracy: 0.8951
'''
|
cs |
'코딩로그 > 모두를 위한 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 9. Neural Network 1: XOR 문제와 학습방법, Backpropagation (0) | 2020.01.27 |
|---|---|
| 8. 딥러닝의 기본 개념과, 문제, 그리고 해결 (0) | 2020.01.11 |
| 7-1. ML의 실용과 몇가지 팁 (0) | 2020.01.11 |
| 6. softmax regression (0) | 2020.01.11 |
| 5. logistic classification (0) | 2020.01.10 |




